Growth Rollout
The following parameters offer granular control over the ivy's surfaces, growth behavior, adhesion properties, and visual characteristics, giving you all the options you need to ensure that the plant interacts realistically with its surroundings.
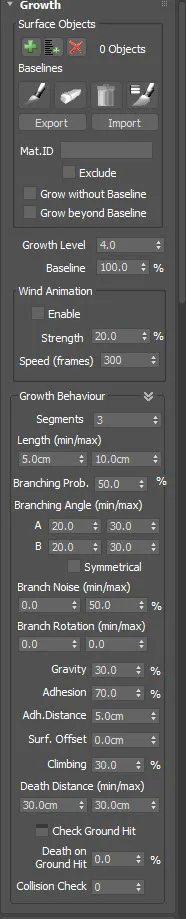
Surface Objects
Assign one or more objects as the growth base then use the Paint tool to draw an initial growing path directly on the surface. Should you need to adjust the positions, use the Erase tool to remove unwanted points and repaint as necessary. Controls include:
- Add Single Surface Objects: Pick a surface where Ivy will grow.
- Add Multiple Surface Objects: Pick a selection of surfaces from the scene where Ivy will grow.
- Delete all Objects: Clears the current selection of objects
- Paint Tool: Used to draw the initial base line on the surface(s).
- Erase: Use to delete base lines from the surface using a brush.
- Delete All: Use to remove all base lines from the surface.
- Painter Options: Used to adjust the brush settings.
- Material ID: Use to limit the polygons on the surface that can be used to grow ivy based on their material IDs. For multiple material IDs, use a comma separated list.
- Exclude: When activated, the list of material IDs is used to exclude parts of the mesh from growing ivy.
- Grow Without Surface: When enabled, the baselines are ignored and a single plant is planted at the ForestIvy object's pivot point. It can be used to make basic shrubs, flowers and other simple plants.
- Grow Beyond Baseline: When enabled, the branches continue to grow from the end of the baselines as well as its sides. When disabled, the length of the baseline is fixed, and new branches only grow from its sides.
- Growth Level: The lifespan of each branch. Larger values simulate a longer growing time for the plant.
- Baseline: Used if you would like to limit the growth along the baseline. For example, a setting of 50% would use only have of the baseline to generate new branches. This parameter can be animated along with Growth Level to create animations.
Wind Animation Parameters
ForestIvy includes a simple wind animation system that allows you to add movement to leaves and branches, creating a more natural look for your vegetation. The animation is controlled by global settings under Growth, with additional per-layer controls for leaves and branches.
Usage
- Enable animation globally from the Growth rollout.
- Adjust Strength to set the intensity of the effect.
- Use Speed (frames) to define the speed of the wind animation. Smaller values result in faster wind and larger values slow the wind down.
- Fine-tune the effect by modifying strength for Leaves and Branches separately.
Interface
- Enabled Toggles wind animation on or off globally.
- Strength Controls the global intensity of the wind animation. Default: 20%.
- Speed (frames) Sets the cycle length of the animation in frames. Lower values make the animation loop faster. Default: 300 frames.
Growth Behavior Parameters
Ivy is formed by multiple branches. Each branch is defined by sections, and each section has a fixed number of segments. When a branch section grows, and its reaches the maximum number of segments, there is a probability that the branch splits into two.The following parameters define this growth behavior:
- Segments per Branch: Defines the segment count per branch section.
- Length: The range between the minimum and maximum length of branch sections. Multiplying this value by the Growth Level will give you an indication of the minimum and maximum size of your plant,
- Branching Probability: The likelihood of a branch section splitting upon reaching the segment limit.
- Branching Angle: Controls the angle between emerging branches, with options for minimum and maximum angles. There are two sets of settings (A and B) that allow you to enter separate controls for the left and right sides of the forked branch.
- Symmetrical Branching: If activated, child branches mirror the angle values for a symmetrical appearance.
- Branch Noise: Adds randomised noise to the branch for a more natural appearance.
- Branch Rotation Introduces additional variation by rotating branches around the trunk or baseline.
Adhesion and Climbing Behavior
These parameters define how the ivy interacts with surfaces, as well as how they transition between clinging and free growth states:
- Gravity: Influences the branch's direction to simulate gravity when the branch is detached from the surface and growing freely.
- Adhesion: The surface attraction level. Higher values mean that the ivy is more likely to cling to the nearest surface.
- Adhesion Distance: The threshold distance dictating the switch between adhered and free growth states.
- Surface Offset: Allows you to push the branches away from the surface, useful if you are using displacement.
- Climbing Factor: Determines the climbing ability over surfaces. Higher values will cause the plant to grow more vertically, lower values allow the plant to spread horizontally.
- Death Distance: The maximum allowed distance from the surface; if a branch exceeds this value, it results in branch termination.
- Check Ground Hit: When enabled, ForestIvy checks collisions with the ground plane and removes branches based on the Death on Ground hit percentage.
- Death on Ground Hit: The percentage of branches that are removed when hitting the ground plane. The ground plane used for this calculation is defined by the pivot position of the ForestIvy object.
- Collision Check: Prevents excessive amounts of geometry by limiting stacked branches. A Value of 0 disabled collision checking but can cause excessive amounts of geometry to be generated.